Learning from the machine: AI assistance is not an effective learning tool for resident education in chest x-ray interpretation
Objectives
To assess whether a computer-aided detection (CADe) system could serve as a learning tool for radiology residents in chest X-ray (CXR) interpretation.
Methods
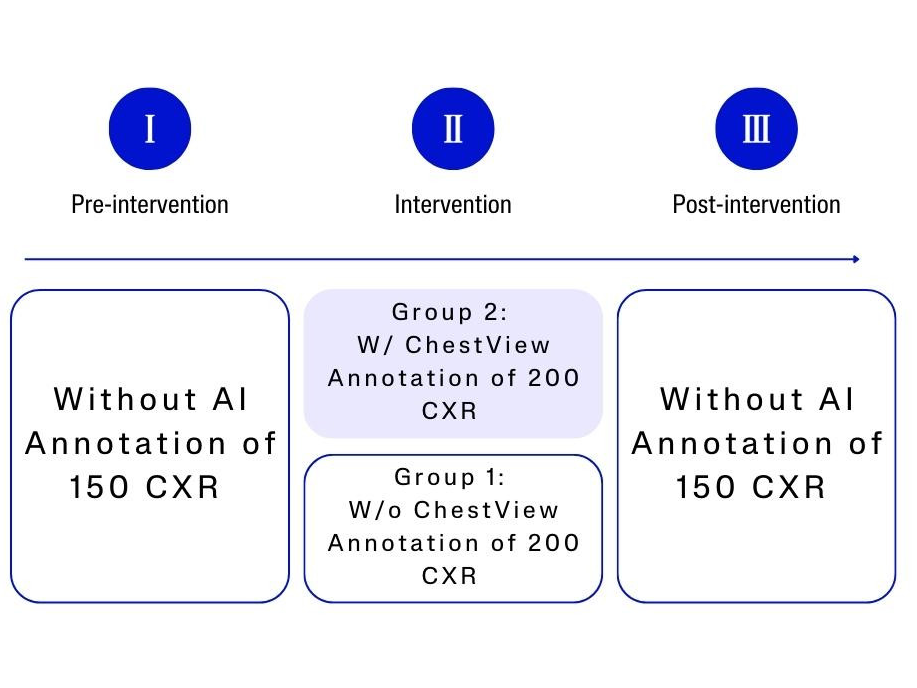
Eight radiology residents were asked to interpret 500 CXRs for the detection of five abnormalities, namely pneumothorax, pleural effusion, alveolar syndrome, lung nodule, and mediastinal mass. After interpreting 150 CXRs, the residents were divided into 2 groups of equivalent performance and experience. Subsequently, group 1 interpreted 200 CXRs from the “intervention dataset” using a CADe as a second reader, while group 2 served as a control by interpreting the same CXRs without the use of CADe. Finally, the 2 groups interpreted another 150 CXRs without the use of CADe. The sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy before, during, and after the intervention were compared.
Results
Before the intervention, the median individual sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of the eight radiology residents were 43% (range: 35–57%), 90% (range: 82–96%), and 81% (range: 76–84%), respectively. With the use of CADe, residents from group 1 had a significantly higher overall sensitivity (53% [n = 431/816] vs 43% [n = 349/816], p < 0.001), specificity (94% [i = 3206/3428] vs 90% [n = 3127/3477], p < 0.001), and accuracy (86% [n = 3637/4244] vs 81% [n = 3476/4293], p < 0.001), compared to the control group. After the intervention, there were no significant differences between group 1 and group 2 regarding the overall sensitivity (44% [n = 309/696] vs 46% [n = 317/696], p = 0.666), specificity (90% [n = 2294/2541] vs 90% [n = 2285/2542], p = 0.642), or accuracy (80% [n = 2603/3237] vs 80% [n = 2602/3238], p = 0.955).
Conclusions
Although it improves radiology residents’ performances for interpreting CXRs, a CADe system alone did not appear to be an effective learning tool and should not replace teaching.
Clinical relevance statement
Although the use of artificial intelligence improves radiology residents’ performance in chest X-rays interpretation, artificial intelligence cannot be used alone as a learning tool and should not replace dedicated teaching.
Key Points
• With CADe as a second reader, residents had a significantly higher sensitivity (53% vs 43%, p < 0.001), specificity (94% vs 90%, p < 0.001), and accuracy (86% vs 81%, p < 0.001), compared to residents without CADe.
• After removing access to the CADe system, residents’ sensitivity (44% vs 46%, p = 0.666), specificity (90% vs 90%, p = 0.642), and accuracy (80% vs 80%, p = 0.955) returned to that of the level for the group without CADe.